Overview
- Serial interface
- Synchronous
- Master-Slave
- Data Exchange
其中Synchronous protocol
- 資料沿著clock(SCK)來傳送
- 當data 需改變及被讀取時,對clock 控制
- 因為是同步(synchronous),所以化的clock rate是可變的,不像RS-232等的通訊
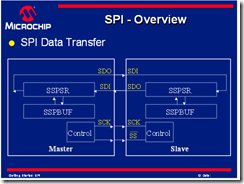
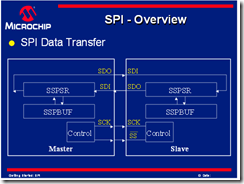
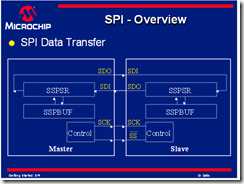
Master-Slave protocol
- 只有一個master可以去控制SCK(clock)
- 直到其clock signal 出現才可以傳送資料
- all slave 都是由master clock來控制
- slave device 可能不會去管clock
Data Exchange protocol
- data is being clocked out,new data is clocked in
- data is exchanged-no device is only transmitter or receive only
- the master controls the exchange by the clock line
它在"transmits" data一筆後,必先去讀取進來的資料,若進來的資料不可讀時
這一筆的資料,就會loss並且其SPI module變成disable as result.
SS(CS) pin define: Slave Select/Chip Select. the master wisch to staart an SPI data exchange between that slave device and itself.
it often used to improve noise (to reset the SPI slave so that it is ready to receive the next byte)
Data(MOSI/MISO): data is only output during the rising or falling edge of SCK.
而data會在相對的負edge(+->-)來latche;並確認資料正確後讀取
pin descritor:
SS(chip Select or Slave Select):
when this signal go to low ,the slave will listend for SPI clock and data
SCK(serial clock):
to control when data in/out
SDO(serial data out):
this signal carries the data sent out of the device.
SDI(serial data input):
this signal carries the data sent into the device.
SSPSR (shift register) for SPI module. it shift data in and out of the device . the data travels in a loop to the next shift register
74HC595+ SPI =expander(output)
&4HC165+SPI=




沒有留言:
張貼留言